For a more detailed look at this topic, please see my online course: Medications for Abortion and Pregnancy Loss. Ever invested in accessible education, here’s a quick breakdown of some of the more common questions I get regarding misoprostol and medication abortion.
Medication management of abortion has been around for decades and is undergoing constant research and development. In many places around the world, it is the fastest growing and most prevalent form of abortion care and considered widely to be safe and effective.
Typically, medication protocols involve a combination of medications:
Mifepristone (RU-486/”The Abortion Pill”) softens the cervix, increases uterine receptivity to prostaglandins, and changes the hormonal makeup in pregnancy so as to no longer support growth and development of the pregnancy. Essentially: it ends the pregnancy.
Misoprostol (brand name Cytotec in North America) softens the cervix, induces strong, rhythmic smooth muscle contractions, including the uterus. Essentially: it expels the pregnancy.
These medications are typically used together as a set protocol in the first trimester of pregnancy and accessed through a medical doctor. However, protocols exist well into the second and early third trimester, and community experimentation has shown alternative administration protocols to be very effective.
One of the more important developments in research around medication abortion protocols is that misoprostol works well to induce an abortion all on its own. Sound, scientific studies have shown that even without Mifepristone, misoprostol alone is safe, effective, and (unlike Mifepristone) much more accessible and affordable.
As perhaps the most researched, and most publicly discussed method of abortion care, medication abortion is often under great scrutiny and regulations that are unreasonable and/or not scientifically sound are pervasive in many communities. These often create misconceptions around these medications and how they work.
Misoprostol is a prostaglandin analogue that binds to myometrial cells, causing contractions of smooth muscle tissue. It is typically used in combination protocols for abortion and miscarriage management as the second step, though also effective alone.
Misoprostol was developed to treat stomach ulcers, but has developed many obstetrical uses, most of which are off-label all over the world, meaning these uses are well-researched and widely used but often not officially approved by drug regulators in that country. This does not stop them from being used for obstetric indications often.
Misoprostol is the drug name, and it goes by many trade names worldwide, including Cytotec, Misoclear, and others.
A new formulation on the market is growing in popularity: Misoprostol mixed with Diclofenac (usually as a hard pill of Diclofenac coated in misoprostol outer layer). Diclofenac is a pain killer. This formulation is meant to treat arthritis.
Protocols when working with Misoprostol Alone:
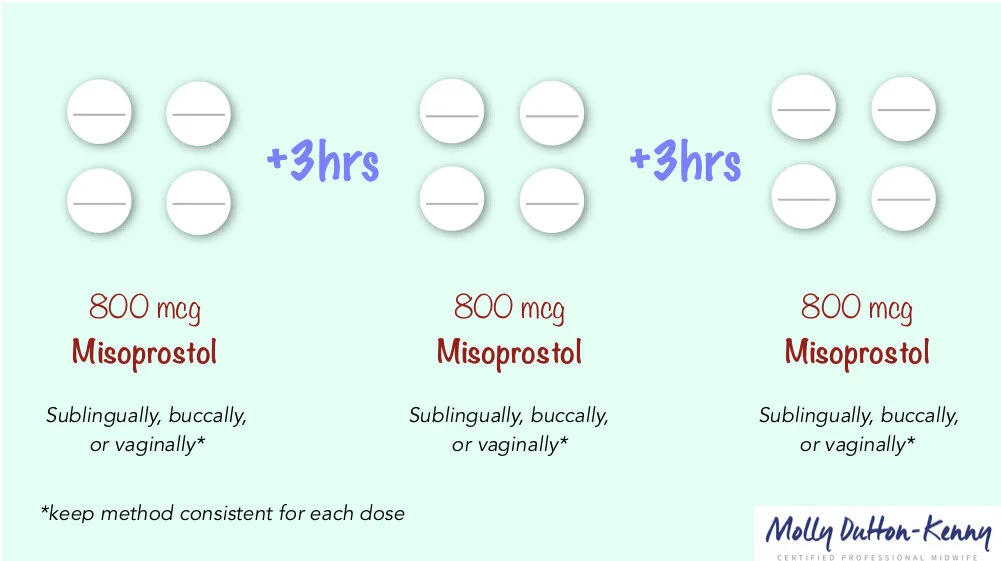
Misoprostol (alone) is most commonly used to end a pregnancy in the first trimester, as follows:
up to 13 weeks LMP:
diagram with protocol
Misoprostol (800mcg), taken orally, sublingually, buccally, or vaginally
Repeat dosing every 3 hours, up to 3 times.
If bleeding is heavy after 1 or 2 doses, may not need to continue to third dose. If bleeding is light or nonexistent after third dose, give the body three days rest, and then repeat whole protocol. Repeat administrations tend to be effective eventually.
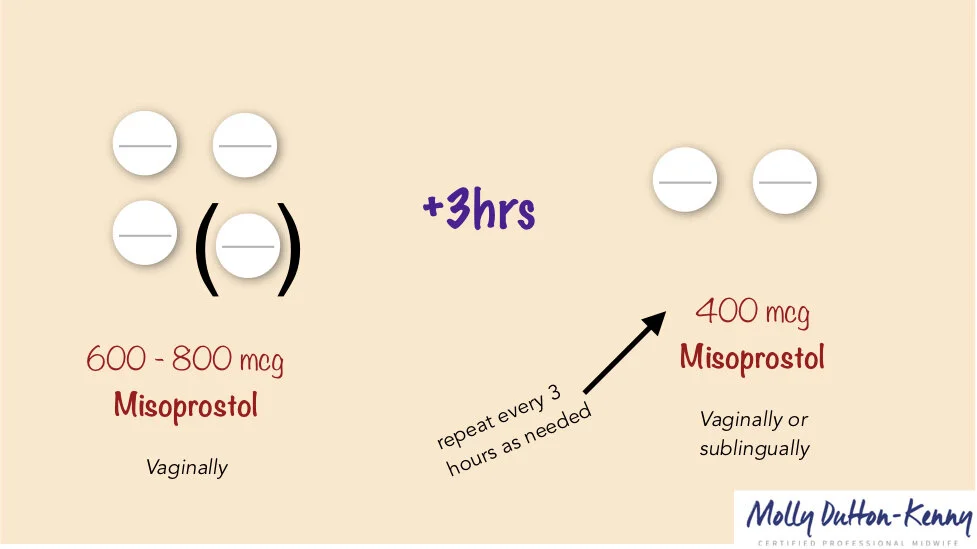
Misoprostol is shown to be equally if not marginally more effective in the second trimester. Typically, the regimen would be as follows:
(between 13-25 weeks LMP):
Misoprostol (600-800mcg) vaginally
3 hours later
Misoprostol (400mcg) vaginally or sublingually
If necessary, repeat doses of Misoprostol (400mcg) vaginally or sublingually every 3 hours to a maximum of 5 doses*
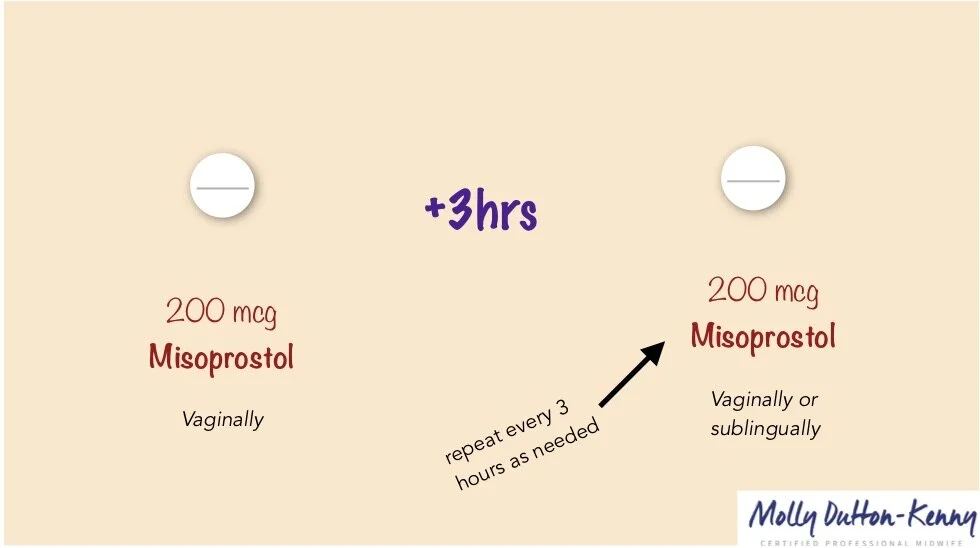
(between 25-28 weeks LMP):
Misoprostol (200mcg) vaginally
3 hours later
Misoprostol (200mcg) vaginally or sublingually
If necessary, repeat doses of Misoprostol (200mcg) vaginally or sublingually every 3 hours to a maximum of 5 doses*
*There are some studies that have tested unlimited dosing regimens when a complete abortion has still not occurred after 5 doses, and most found a complete abortion, with the same picture of safety, in about 7-8 doses.
You’ll note that the dosage of Misoprostol is typically 800mcg in the first trimester and LESS (200-400mcg) in the second trimester. For many this feels counterintuitive: wouldn’t you need more medication as the pregnancy advances? Actually, as the uterus grows, it has more receptors to react to the medication, so less medication is needed to achieve the same result. Overloading a growing uterus can be dangerous. Lower doses, but more of them (rather than fewer high doses) is considered much safer.
How Should the Doses Be Taken?
While some protocols specify the best route of taking the medications, others allow for multiple choices. How to best choose?
Misoprostol can be taken four different ways:
Orally (swallow it whole, followed by water)
Sublingually (hold it under your tongue to dissolve)
Buccally (pack it between your cheeks and your gums to dissolve)
Vaginally (insert vaginally as high up as you can get them)
You may see descriptions in the literature of misoprostol being given rectally: this used to be common practice for managing postpartum hemorrhages, but is no longer best practice. This route of administration is not recommended for abortion or pregnancy loss.
The most commonly recommended ways are sublingual and vaginal for the primary reasons that they are easier to explain (people often get tripped up explaining buccal administration) and they have fewer side effects (than oral administration).
Taking it orally works the fastest but has the most side effects, so it is generally not recommended.
Taking it sublingually works pretty fast and has minimal to moderate side effects.
Taking it buccally works pretty fast and has minimal to moderate side effects.
Taking it vaginally works the slowest (up to 24 hrs delay) and has the fewest side effects.
How you take it may be a personal choice, or may be specifically recommended based on gestation and circumstance.
diagram for research-based misoprostol-only protocols for a variety of circumstances and gestations from FIGO, the international organization of Obstetricians/Gynecologists.
Efficacy
When used for the purposes of first trimester abortion, medication abortion protocols are effective (roughly) as follows:
Mifepristone + Misoprostol: 95-98% effective
Methotrexate + Misoprostol: 90-97% effective
Misoprostol Alone: 80-90% effective
When using medications for first trimester miscarriage or abortion, if you fall in the small category of people it was not effective for, you can wait three days, and repeat the whole protocol again. In almost all cases, I’ve seen it be effective the second time around.
When used for second trimester abortion, medication abortion protocols typically only include misoprostol, though emerging evidence is showing the value of adding Mifepristone, too. The stats for the second trimester currently show:
Mifepristone + Misoprostol: 96-98% effective
Misoprostol alone: 90% effective
As more and more studies are done pushing limits on how many doses may be administered safely, research is showing near total efficacy in the second trimester when unlimited proper dosing is offered, under careful supervision.
For More Information
For a comprehensive look at Medication Abortion including exploring Mifepristone, Misoprostol, and Methortreaxate for both abortion and pregnancy loss, including:
Histories and Contexts
Current Events and Developments
Effects and Side Effects
Troubleshooting and Complications
Considerations and Contraindications
How to prepare to support the body before, during, and after
How to research this topic well
And more…
Check out my Course:
(Approx 4-5 hrs content). In this course we take a look at three primary medications used for abortion, miscarriage, and pregnancy loss: Mifepristone, Methotrexate, and Misoprostol. We look at these medication’s histories, physiologies, pharmacokinetics, how we can expect them to work in our bodies, proper dosing across circumstances of pregnancy and all trimesters, effects and side effects, preparing our bodies, experiencing release, and recovery. We also look at troubleshooting and complications, considerations and complications, current events, gathering good quality information, access chains and local networks. We also have a lively and vulnerable Q&A!